Incident Response and Threat hunting with OSQuery and Fleet
In this guide, we are going to explore some powerful tools to help you enhance your incident response and threat hunting assessments. These tools are OSQuery and Kolide Fleet.
 Image source: OSQUERY logo
Image source: OSQUERY logo
Let's start exploring the first tool OSQuery
OSQuery Overview
According to its official Github repository:

Osquery is a __ __ SQL __ __ powered __ __ operating system __ __ instrumentation, __ __ monitoring __, and__ __analytics__ __framework. It is Available for__ __Linux__ , __ __ macOS __,__ __Windows,__and FreeBSD.
Its official website is https://osquery.io
To download OSQuery visit: https://osquery.io/downloads/official/4.3.0
For the demonstration, we are going to use a Ubuntu 18.04 TLS server machine. To install it on our Ubuntu server type the following commands:
export OSQUERY\_KEY=1484120AC4E9F8A1A577AEEE97A80C63C9D8B80B
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-keys $OSQUERY\_KEY
sudo add-apt-repository 'deb [arch=amd64] [https://pkg.osquery.io/deb](https://pkg.osquery.io/deb) deb main'
sudo apt-get update
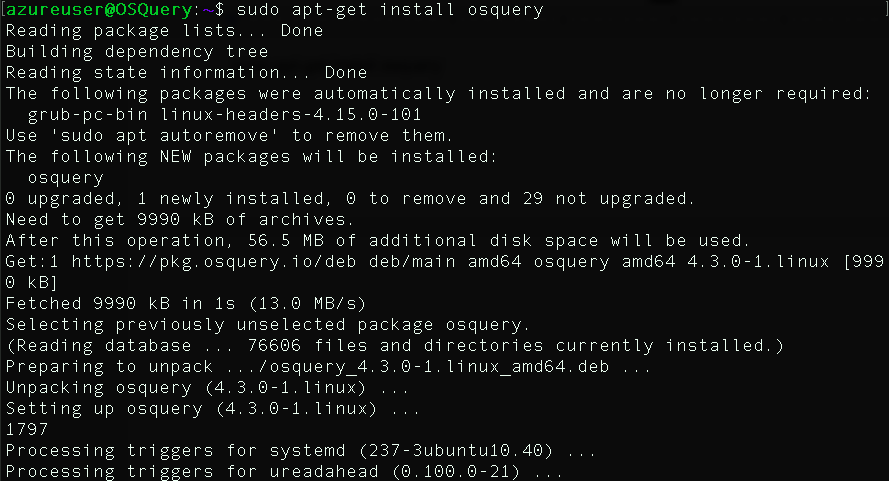
sudo apt-get install osquery
OSQuery delivers these modes:
- Osqueryi: Interactive shell
- Osqueryd: Deamon
To start using OSQuery simply type:
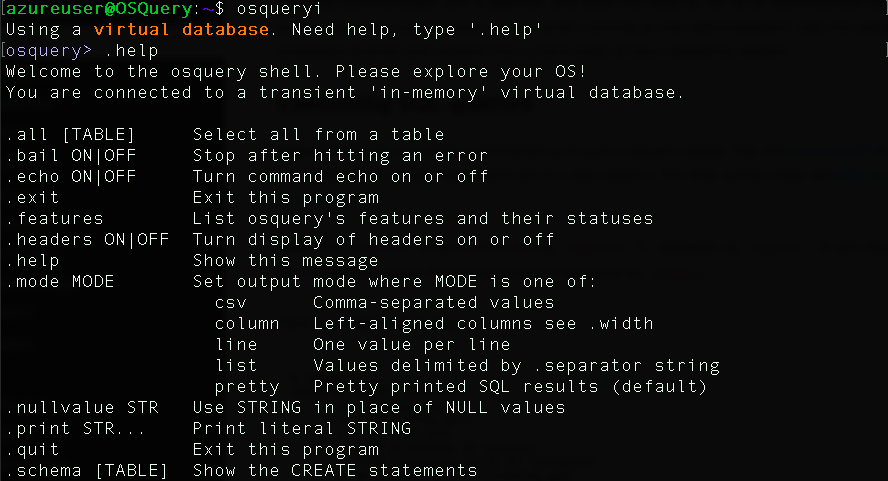
osqueryi
To explore the available commands type .help
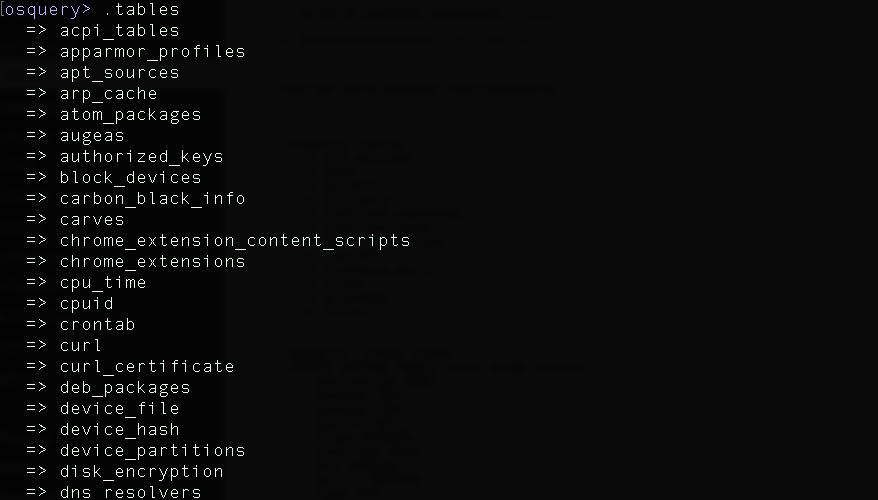
To explore the available tables type
.tables
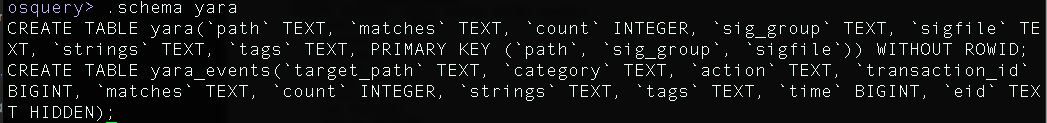
To explore the schema of a specific table type
.schema <TABLE_HERE>
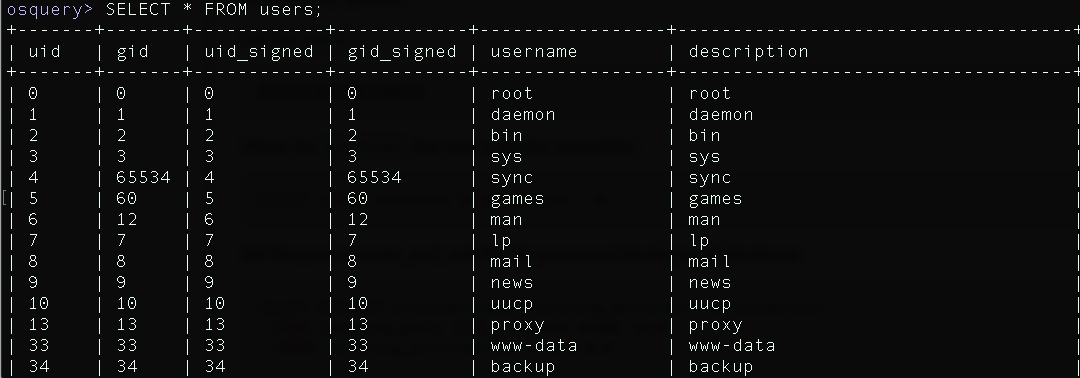
For example if you want to get the users type:
select * from users ;
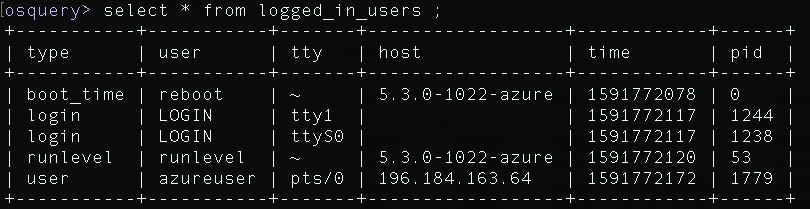
To select loggedin users type:
select * from logged_in_users ;
The official website contains the list of all the available tables and its schemes. For example this is the scheme of Kernel_info table
For example to select the version of the kernel type:
select version from Kernel_info
Let's suppose that you want to automate a specific query (selecting users) every 300 seconds. Edit the /etc/osquery/osquery.conf file and add your rules
"schedule": { "Users": { "query": "SELECT * FROM users;", "interval": 300 } },
A collection of queries is called a Pack. OSQuery provides many hekpful packs that you can use in your assessments here: https://github.com/osquery/osquery/tree/master/packs
This is a query from https://github.com/osquery/osquery/blob/master/packs/incident-response.conf that retreive all the startup items in MacOS hosts:

But now, what to do if we want to deploy OSQuery in large scale environments and we want to manage them all easily. In this situation we need another powerful platform called "Kolide Fleet"
Kolide Fleet (OSQuery Management)
:heavy_exclamation_mark: Kolide is no longer maintaining Fleet. The new name is Fleet and can be found here: https://github.com/fleetdm/fleet

Fleet is the most widely used open source osquery manager. Deploying osquery with Fleet enables programmable live queries, streaming logs, and effective management of osquery across 50,000+ servers, containers, and laptops. It's especially useful for talking to multiple devices at the same time.

According to its official Github repository:
Fleet is the most widely used __ __ open-source __ __ osquery Fleet manager. Deploying osquery with Fleet enables live queries, and effective __ __ management __ __ of osquery infrastructure.
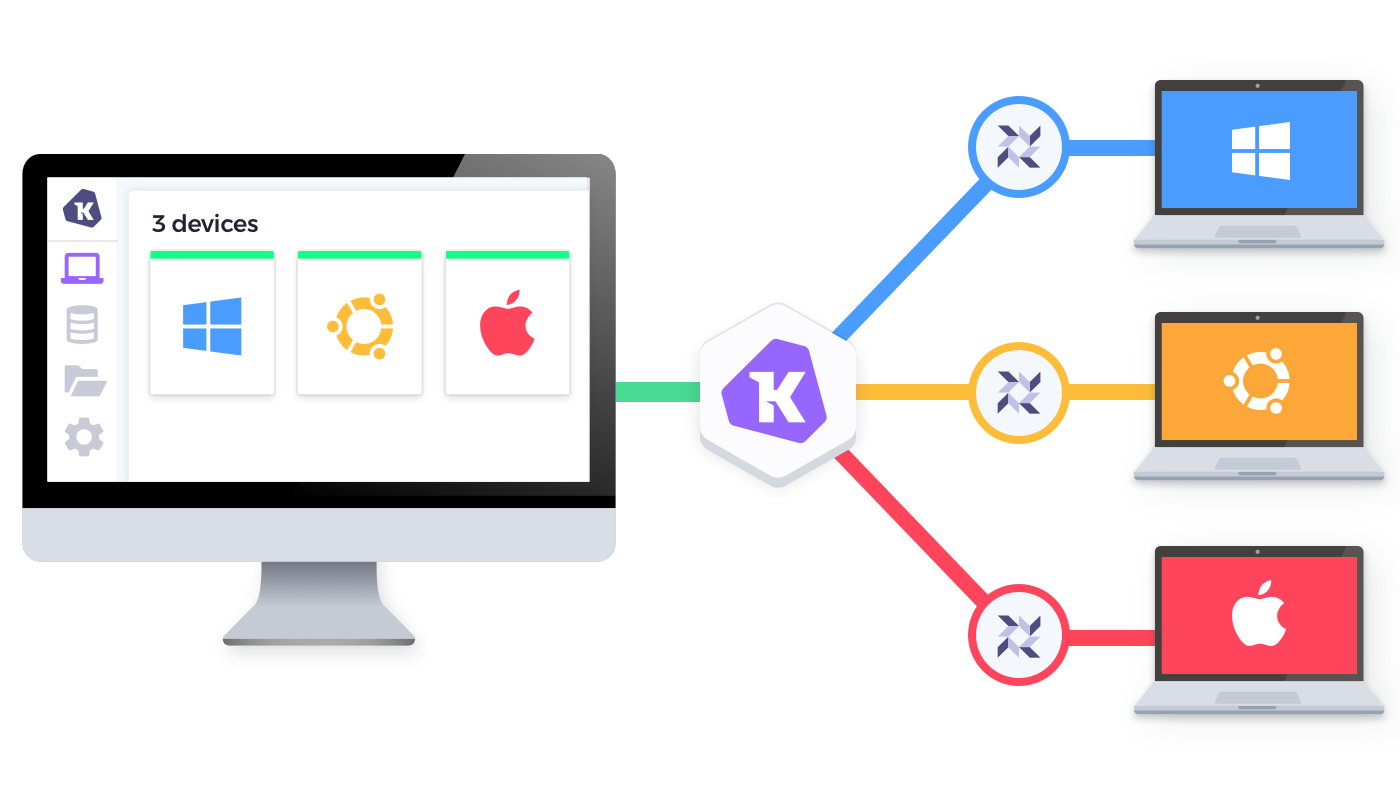 Image source: Kolide fleet
Image source: Kolide fleet
To install it use the following commands:
wget https://github.com/kolide/fleet/releases/latest/download/fleet.zip
sudo apt-get install unzip
Unzip the file:
sudo unzip fleet.zip
Enter the linux folder:
Copy the binaries in /usr/bin
sudo cp * /usr/bin/
Install this required program:
sudo apt install software-properties-common
sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 0xF1656F24C74CD1D8
add-apt-repository 'deb [arch=amd64,arm64,ppc64el] http://sfo1.mirrors.digitalocean.com/mariadb/repo/10.4/ubuntu bionic main'
sudo apt-get update
Install Maria database server and its client:
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client
Check its status:
sudo systemctl status mariadb
Enable Mariadb service:
sudo systemctl is-enabled mariadb
Enter mysql and type the following commands:
sudo mysql -u root -p
create database kolide;
grant all on kolide.* to kolideuser@localhost identified by 'Passw0rd!';
flush privileges;
exit
Install Redis:
sudo apt install redis
Prepare fleet:
fleet prepare db --mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 --mysql_database=kolide --mysql_username=kolideuser --mysql_password=Passw0rd!
fleet serve --mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 \
--mysql_database=kolide --mysql_username=kolideuser --mysql_password=Passw0rd! \
--server_cert=/etc/ssl/certs/kolide.cert --server_key=/etc/ssl/private/kolide.key \
--logging_json
sudo fleet serve --mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 \
--mysql_database=kolide --mysql_username=kolideuser --mysql_password=Passw0rd! \
--server_cert=/etc/ssl/certs/kolide.cert --server_key=/etc/ssl/private/kolide.key \
--logging_json --auth_jwt_key=9yKI2MeThUSLtsYiCS7etUSJZD1lgHLr
Start fleet:
Go to https://\<SERVER_IP\>:8080
Provide your username, password and email
Add your organization name, the organization domain name/IP and submit:
Voila! Kolide fleet is deployed successfully.
Now let's add our host. To do so, click on "ADD NEW HOST" and you will get this window. It provides a key called "OSQuery enroll secret" that we are going to use later.
To add the host, we need to install the fleet launcher. In our case we are using the same host.
wget https://github.com/kolide/launcher/releases/download/v0.11.10/launcher_v0.11.10.zip
Unzip the file:
sudo unzip launcher\_v0.11.10.zip
Enter the Linux file:
cd linux
Start the launcher
./launcher --hostname=127.0.0.1:8080 --root_directory=$(mktemp -d) --enroll_secret=<COPY SECRET KEY HERE> --insecure
Congratulation! if you refresh the Kolide fleet dashboard you will see the newly added host
To run and add queries go to QUERY -\> New Query
Type the SQL Query
Select the targets/hosts
Click on "Run". You will get the query outputs below: